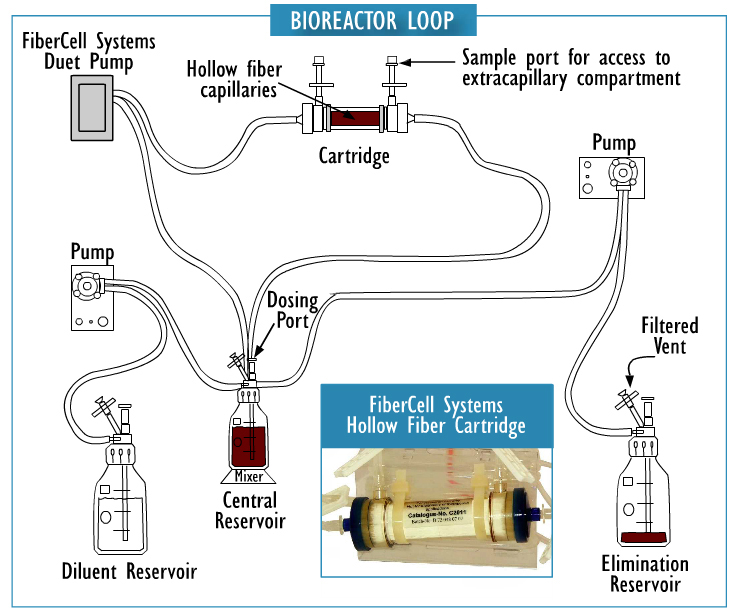
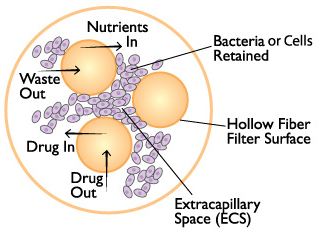
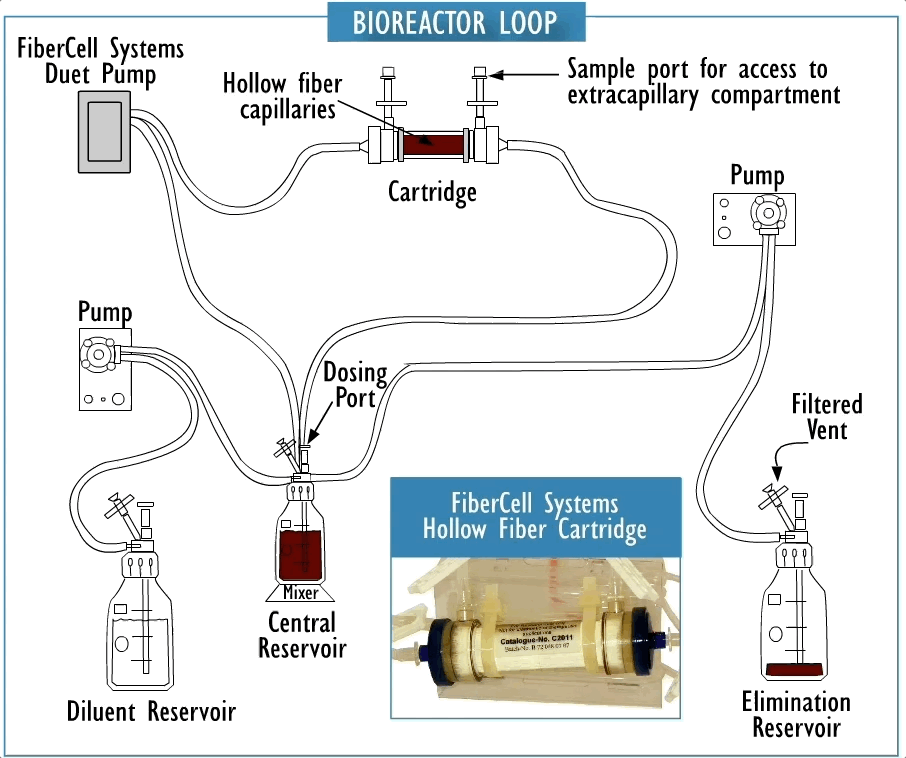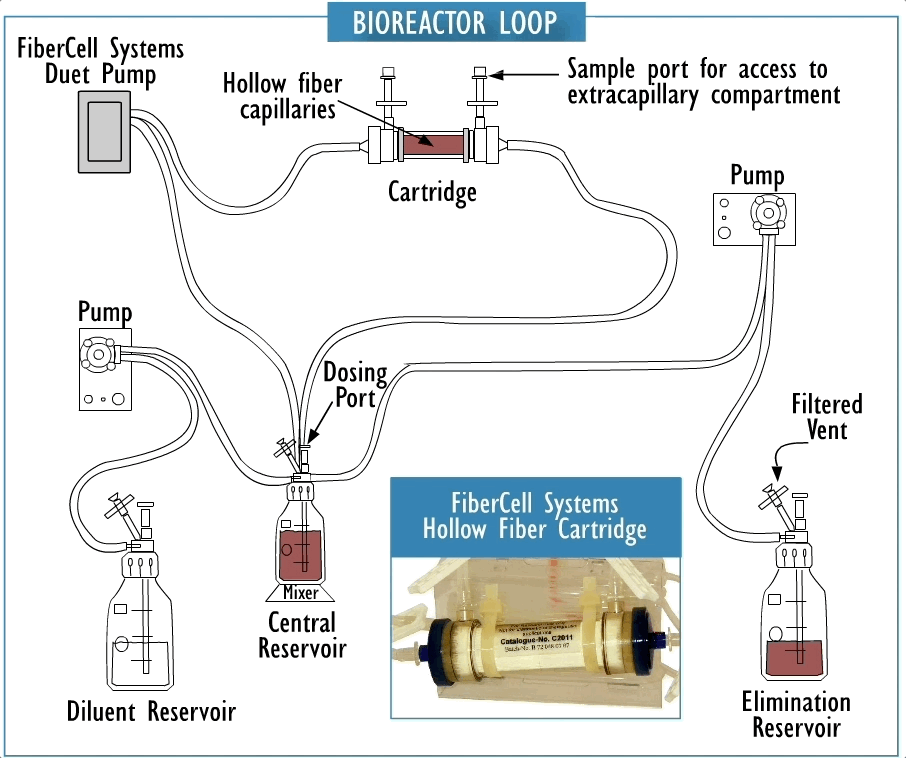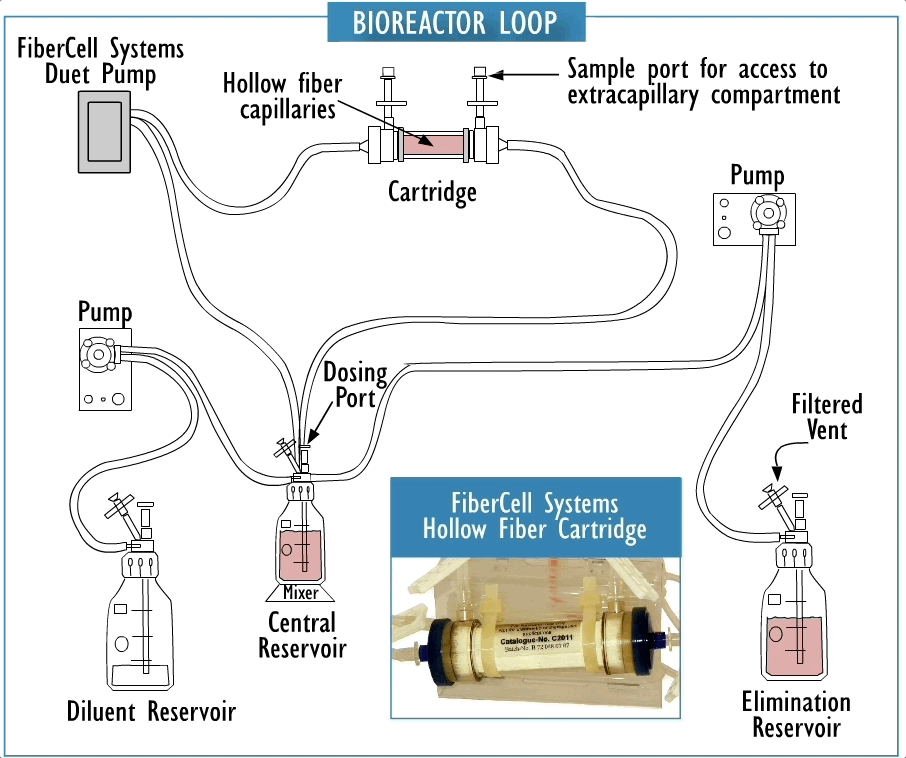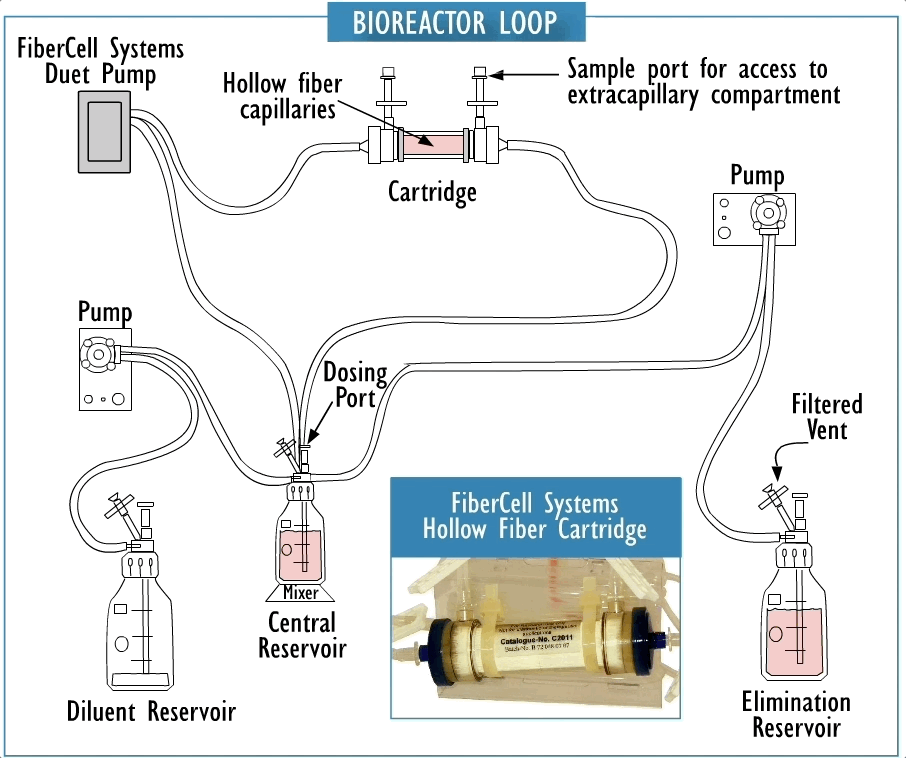
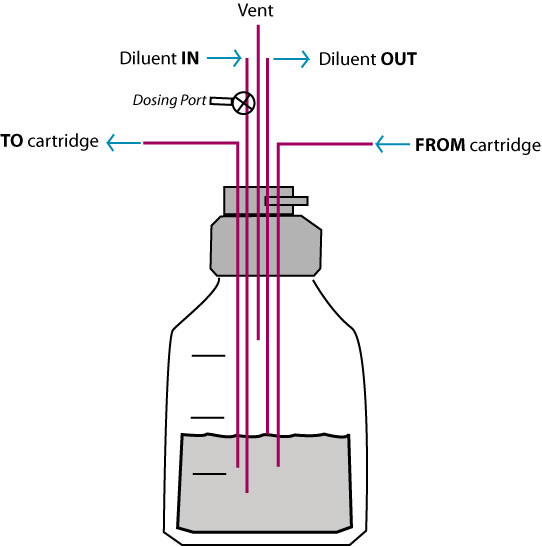
Cross section of a hollow fiber cartridge. The test organism is retained in the small volume outside the fiber while nutrient broth and drug circulate through the insides of the fiber. Small molecules such as drugs can freely cross the fiber along with nutrients and waste products, while bacteria and cells cannot cross the fiber.



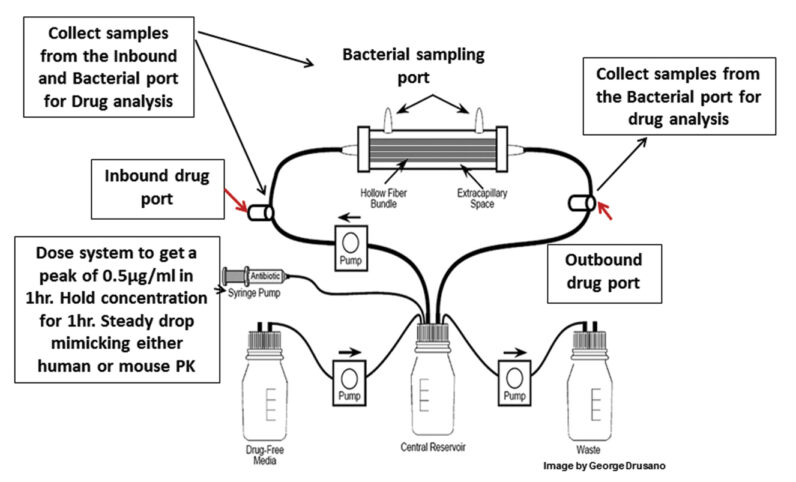
Hollow fiber technology offers higher levels of reproducible control of both concentration and time of drug exposure in complex growth, infection, treatment, and sampling regimens. This system permits more realistic simulation of in-vivo drug effects in a dynamically controlled system providing data that more accurately reflects biological responses.
They are fully disposable and provide a biosafe environment for the potential testing of drug resistant, weaponized, or genetically modified organisms. The two-compartment model can be a cost effective supplement to the evaluation of clinical efficacy both for existing antibiotics and in the development process for new antibiotics as part of the submission process for FDA approval.
Web Application for Pump Settings
An R-shiny web application, was developed to facilitate the conversion of in-vivo pharmacokinetic profiles into in-vitro pump settings in the hollow fiber system.
Click here to use it: https://pkpdia.shinyapps.io/hfs_app/
Source: Mimicking in-vivo exposures to drug combinations in-vitro: antituberculosis drugs in lung lesions and the hollow fiber model of infection: Kloprogge, F. et al, www.nature.com/scientificreports 13 Sep 2019 [open access]
Suggested Ordering for Antibiotic PK/PD:
| Bioreactor | ||||||||
| P3202 | The FiberCell® Systems Duet more info | |||||||
| Cartridges | ||||||||
| Catalog No. | Size | Surface Area | Fiber Type | Packing Density | ECS Vol | MWCO 50% | Max. Cell# | |
| C2025D | Small | 450 cm2 | High flux PS | 50% | 3.2 mL | 20 kD | 108 | more info |
| C2011 | Medium | 4000 cm2 | High flux PS | 50% | 15 mL | 20 kD | 109 | more info |
| C8008 | Medium | 2500 cm2 | Cellulosic | 40% | 5 kD | 5x10e8 | more info | |
| Reservoir Caps | ||||||||
| A1006 | 38 mm Reservoir Cap more info | |||||||
| A1007 | 5 port 38mm Reservoir Cap more info | |||||||
Click here for our US list pricing for 2023. We offer tiered discounted pricing for quantity purchases of our products, 10-25 units, 25+ units, and 50+ units. Please enquire for details. We recommend the most appropriate products for your applications so please feel free to email or phone us to discuss your application and provide you with a quote at info@fibercellsystems.com, 301-471-1269, 240-440-2662. We can accept credit cards and purchase orders from accredited institutions.


1. The Hollow Fiber Infection Model, Principles and Practice
Emerging antibiotic resistance presents a serious global health threat and has been identified as one of the three greatest threats to human health. Antibiotic discovery and development require static susceptibility testing to screen compounds, in vitro pharmacodynamics/pharmacokinetic (PK/PD) studies to model drug dynamics and efficacy, and testing in animal models to provide critical information prior to the clinical evaluation of new antibiotics. Read paper here.
2. EMA endorsement
The EMA has endorsed FiberCell’s in-vitro hollow fiber system model of tuberculosis (HSF-TB) for use in drug development. See endorsement here.
3. The Hollow Fiber Infection Model for Antimicrobial Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
PK/PD assays are one of the first steps in determining the potential utility of a specific compound for antimicrobial activity. The Hollow Fiber Infection Model can provide useful data for antibiotic development and dosing. Hollow fiber technology offers higher levels of reproducible control of both concentration and time of drug exposure in complex growth, infection, treatment, and sampling regimens. Read paper here.